Tapable hooks
Tapable hooks in server
It’s an important step of the HTTP servers using server renderers of web user interface libraries such as vue/server-renderer and react-dom/server to render web applications to strings or streams during SSR (server side rendering). Vise is built around the SSR process.
It’s also important that web applications may need other logics on the server during SSR such as:
- Fetch data from APIs used in page rendering.
- Caching and reusing of SSR HTML.
- Error handling like fail to fetch data or 404 visit.
- Generation of HTML fragments outside the
<App>tag. - Statistics and reporting of data.
Some of these logics could be put in hooks of web user interface libraries such as created, but the downside is that server logic and client logic are mixed. Sometimes they have totally different 3rd party dependencies, which may cause the generated client bundle to contain unnecessary sever packages and impact user experience.
Another way is putting those logics in HTTP servers, which is the early choice of Vise. But it’s proved to cause scalability issues, since as the apps grows bigger and more apps deployed on the sever, the codes written in the HTTP servers could easily lose control.
Vise defined the server life cycle, which is based on tapable and exposes multiple hooks from the point a server receiving an HTTP request from the user to the server sending the HTTP response of the request:
- Server logics of certain app belongs to the app but not the HTTP server anymore.
- Server-only packages do not exist in the generated client bundles.
- Multiple apps could be deployed in the same server and scale up.
- Hooks are standard, flexible and extendable. Certain server side process could be abstracted as an Vise hooks plugin composed of several coordinated hooks and be reused easily.
Vise Server Hooks Lifecycle
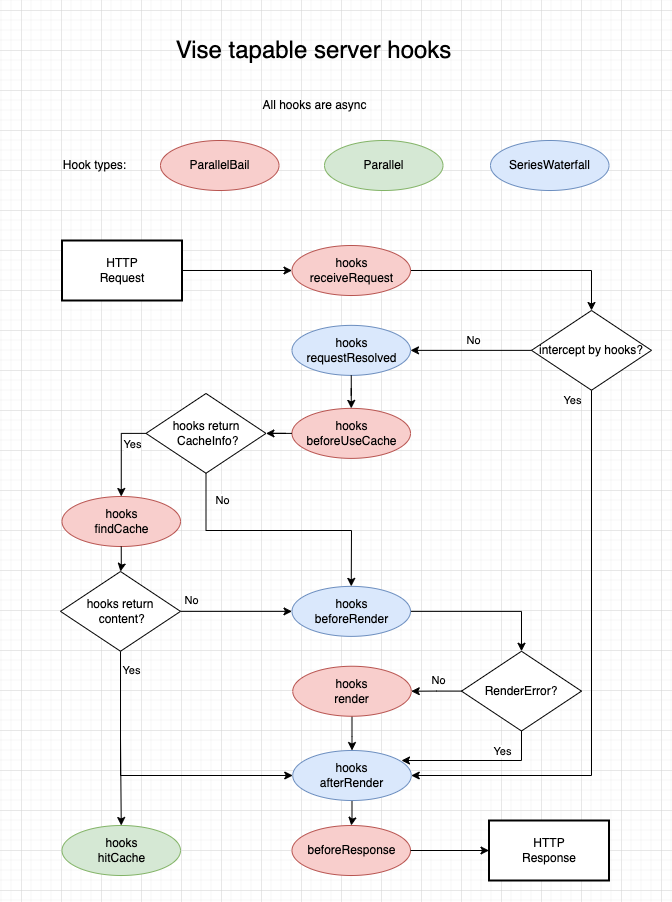
Vise defined 9 tapable hooks:
- hooks.receiveRequest
- hooks.requestResolved
- hooks.beforeUseCache
- hooks.findCache
- hooks.hitCache
- hooks.beforeRender
- hooks.render
- hooks.afterRender
- hooks.beforeResponse
Hooks Detail
receiveRequest
HTTP requests could be intercepted in this hook after server received it from clients. Bypass the default SSR is possible by return a custom RenderResult.
Any tapped function returns RenderResult will invalidate the return value of other tapped functions.
If default rendering is bypassed, the next hook is hooks.afterRender.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| Name | receiveRequest |
| Hook Type | AsyncParallelBailHook |
| Parameters | HTTPRequest |
| Return Value | Omit<RenderResult, ‘type’ | ‘renderBy’> | void |
hooks.requestResolved
Tapped functions receive a ResolvedRequest and return a ResolvedRequest. Marks could be added to context of certain requests for later process. Be careful of hydration mismatch if you change data in the HTTPRequest.
Multiple tapped functions execute one by one in order.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| Name | requestResolved |
| Hook Type | AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook |
| Parameters | ResolvedRequest |
| Return Value | ResolvedRequest |
hooks.beforeUseCache
Tapped function calculate CacheInfo from RenderContext, which will be used to find previous cached SSR data or save newly generated SSR data.
Any tapped function return CacheInfo will invalidate the return value of other tapped functions.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| Name | beforeUseCache |
| Hook Type | AsyncParallelBailHook |
| Parameters | RenderContext |
| Return Value | CacheInfo | void |
hooks.findCache
Find previously cached SSR data with CacheInfo.
Any tapped function return string will invalidate the return value of other tapped functions.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| Name | findCache |
| Hook Type | AsyncParallelBailHook |
| Parameters | CacheInfo |
| Return Value | string | void |
hooks.hitCache
Tapped functions will be notified with a successful cache hit event.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| Name | hitCache |
| Hook Type | AsyncParallelHook |
| Parameters | HitCache |
| Return Value | void |
hooks.beforeRender
Tapped functions will be called in order before rendering HTML with server renderer provided by web UI libraries. Typically this could be used to fetch data for SSR. Data should be transferred in RenderContext.extra.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| Name | beforeRender |
| Hook Type | AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook |
| Parameters | RenderContext |
| Return Value | RenderContext |
hooks.render
HTTP server should tap this hook, import app’s render bundle and render the HTML with data in RenderContext. Applications generally don’t use this hook unless custom rendering is expected.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| Name | render |
| Hook Type | AsyncParallelBailHook |
| Parameters | RenderContext |
| Return Value | RenderResult |
hooks.afterRender
Tapped functions will be called in order after render finishes, processing the result of a successful rendering or handle the error of a failed rendering. Failed SSR could be downgraded to CSR here. Be careful of hydration mismatch.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| Name | afterRender |
| Hook Type | AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook |
| Parameters | RenderResult |
| Retuan Value | RenderResult |
hooks.beforeResponse
Tapped functions will be called after afterRender. This is the last hook before HTTP Response is sent and it’s mainly used for composing the HTTP Response, which could be generated with all data in the RenderResult containing the RenderContext.
Any tapped function returns an HTTPResponse will invalidate the return value of other tapped functions.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| Name | beforeResponse |
| Hook Type | AsyncParallelBailHook |
| Parameters | RenderResult |
| Return Value | HTTPResponse | void |
Hooks Usage
App developer
App developers can use Vise command line tool to create scaffold of an app, then there will be a app directory as described in App Directory Structure.
Then app’s logics could be added to the app-my-project/src/server-hooks.ts file. Typically you’ll want preload data in the beforeRender hook.
server-hooks.ts config
A Typical server-hooks.ts is as following:
import {
ViseHooks,
mergePartial,
fillSsrTemplate,
} from 'vise-ssr';
import { SIDEBAR_ITEMS } from './data/consts';
import request from './utils/request';
/**
* All hook callbacks could be function or array of functions
* Notice: request.url will only include relative path without appName and domain. For example,
* dev path: http://127.0.0.1:3000/page-a/
* online path: https://example.com/path/to/app-name/page-a/
* all match to request.url === '/page-a/'
*/
const serverHooks: ViseHooks = {
appName: 'vue3-intro',
plugins: [], // Vise hooks plugin
/**
* HTTP requests could be intercepted in this hook after server received it from clients
* Bypass the default SSR is possible by return a custom `RenderResult`
* Marks and data should be put in renderResult.context.extra
*/
receiveRequest: [async (httpRequest) => {
let result;
if (httpRequest.url === '/hook-test') {
result = {
context: {
request: httpRequest,
extra: { // add marks to context.extra
jumpTo: 'https://www.vise.com/',
},
},
};
}
return result;
}],
/**
* Tapped functions receive a `ResolvedRequest` and return a `ResolvedRequest`.
* Marks could be added to context of certain requests for later process.
* Be careful of [hydration mismatch] if you change data in the HTTPRequest.
*/
requestResolved: async (resolvedRequest) => {
const { original, resolved } = resolvedRequest;
const { url } = original.request;
const extraData: Record<string, string> = {};
if (url === '/hook-jump') {
extraData.injectByHook = 'RequestResolved inject';
}
return mergePartial(resolvedRequest, {
resolved: {
extra: extraData,
}
});
},
/**
* Tapped function calculate `CacheInfo` from `RenderContext`
* Which will be used to find previous cached SSR data or save newly generated SSR data.
*/
beforeUseCache: async (renderRequest) => {
const { url, headers } = renderRequest.request;
const userAgent = headers['user-agent'] || '';
let result;
// suppose generated html depends on browser is chrome or not
const browser = userAgent.indexOf('Chrome') > -1 ? 'chrome' : 'other';
// cache html by page
if (url === '/' || SIDEBAR_ITEMS.find(item => `/${item.id}` === url)) {
result = {
key: `${browser}_${url}`,
expire: Date.now() + 3600 * 1000,
stale: true,
context: renderRequest,
};
}
return result;
},
// Tapped functions will be notified with a successful cache hit event.
hitCache: async (hitCache) => {
console.log(`Use cache with key: ${hitCache.key}`);
},
/**
* Tapped functions will be called in order before rendering HTML with server renderer provided by web UI libraries
* Typically this could be used to fetch data for SSR. Data should be transferred in `RenderContext.extra`
*/
beforeRender: async (renderContext) => {
// request data for index page
if (renderContext.request.url === '/') {
const apiResult = await request({
url: 'https://www.randomnumberapi.com/api/v1.0/random?min=1000&max=9999&count=1',
});
return mergePartial(renderContext, {
meta: {
initState: apiResult
},
});
}
return renderContext;
},
/**
* Tapped functions will be called in order after render finishes
* Processing the result of a successful rendering or handle the error of a failed rendering.
* Failed SSR could be downgraded to CSR here.
* Be careful of [hydration mismatch].
*/
afterRender: async (renderResult) => {
if (renderResult.type === RenderResultCategory.render) {
if (renderResult.context.request.url === '/hook-jump') {
const newSsrResult = mergePartial<typeof renderResult.ssrResult>(
renderResult.ssrResult,
{
ssrContext: {
title: 'render finish override2',
},
},
);
return {
...renderResult,
ssrResult: {
...newSsrResult,
html: fillSsrTemplate(newSsrResult.template, newSsrResult),
},
};
}
} else if (renderResult.type === RenderResultCategory.error) {
const err = renderResult.error;
return mergePartial(renderResult, {
error: {
// handle error in beforeResponse hook
message: err.code === 404 ? (err.detail!.reason as string) : err.message,
},
});
}
return renderResult;
},
/**
* Tapped functions will be called after `afterRender`
* This is the last hook before HTTP Response is sent
* and it's mainly used for composing the HTTP Response
* Which could be generated with all data in the
* `RenderResult` containing the `RenderContext`
*/
beforeResponse: async (renderResult) => {
if (renderResult.type === RenderResultCategory.render) {
return {
code: 200,
headers: {
'content-type': 'text/html;charset=utf-8',
},
body: renderResult.ssrResult.html,
};
}
// request intercepted by receiveRequest hook
if (renderResult.type === RenderResultCategory.receiveRequest) {
if (renderResult.context.request.url === '/hook-test') {
return {
code: 302,
headers: {
location: 'http://127.0.0.1:3000/hook-jump',
},
};
}
}
if (renderResult.type === RenderResultCategory.error) {
// fallback to CSR when error
result = {
code: 302,
headers: {
location: 'http://example.com/path/to/csr',
},
};
}
},
};
export default serverHooks;
From the example we could see:
- All hooks could be tapped multiple times. Different logics in the same hook lifecycle could be decoupled in different callbacks
- The default export value is constraint by the
ViseHookstype, all parameter and return value types could have IDE notice. - Vise defined multiple data types in the lifecycle such as
HTTPRequest,HTTPResponse,RenderContext,ResolvedRequest,RenderResultto support data transmission during multiple hooks, all these types could be imported from vise-ssr package. More detail at: Key Data Types - A typical operation in a tapped function is to modify a small part of a complex data structure such as
RenderContext. Vise providedmergePartialutil function with deep partial type support to help.
HTTP Server Developer
Core Hook Classes
Vise defined multiple hook related Classes which HTTP Server developer need to understand and use:
- HookLifeCycle: accept
ViseHooksconfig which contains all the tapped functions as parameter, defined whole SSR life cycle. The HTTP Server should create an instance with merged ViseHooks config and hand over the HTTP request to it. - HookManager: define core hook data structure, hook type, tapped function I/O data type
- HookCaller: responsible to call certain hook and log active tapped function activities
- HookLogger: Default logger which provide brief information in the HookLifeCycle, could be overridden
- HookPlugin: support Vise Plugin which combines several tapped functions of different hooks to accomplish a related goal
Merge Config as HookConfig
Applications, HTTP Servers, Plugins all have some logic to be executed in the HookLifeCycle, these logics defined in the form of ViseConfig need to be merged as HookConfig.
- hooks has 3 types: AsyncParallelBailHook, AsyncParallelHook, AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook
- For the Bail type hook, first tapped function returns value will invalidate others’, server developer may need to create higher order functions to avoid conflict between apps and the server
- For Waterfall type hook, execution order is critical. HTTP server may want their own tapped functions to be executed as the last one, so remember to add the enforce config correctly
- In fact, in HookLifeCycle, not only HTTP server’s logic is wrapped as a plugin, the app’s logic is also wrapped as a plugin. HookLifeCycle will then parse and standardize all plugins as
HookConfigwith the right order.
Code Example
// my-server.ts
// ...
const serverHookConfig: Partial<HookCallback> = {
// server specific hooks logic
render(renderContext) {
// import app's render bundle and render it to string
return renderResult;
},
// ...
};
const appHookConfig = await this.loadAppViseHooks(); // load app's server-hooks.ts
const hookLifeCycle = new HookLifeCycle(
addServerHooksAsPlugin( // wrap server's hooks config as a plugin
appHookConfig,
serverHookConfig,
),
new HookLogger(log), // logger could be replaced here
);
express().use('*', async (req, res) => {
// start HookLifeCycle with HTTP request
const response = await hookLifeCycle.start({
url: req.originalUrl,
headers: req.headers,
body: req.body,
});
sendResponse(res, response);
});
Hooks Plugin Developer
Plugin Developer can use several hooks to complete a certain goal, warp it as a plugin with it’s own config for reuse.
Conventions
A Vise Hooks Plugin should:
- has a packaged name of:
vise-hooks-plugin-${myPluginName}, myPluginName should only contain small case letter, number and hyphen(-) - has a default export with VisePlugin type or a function accept a config and return a VisePlugin
Hooks Plugin Example
HTML Cache plugin
This plugin taps
hooks.beforeUseCache,hooks.findCache和hooks.afterRenderhooks, allow user to provide it’s cache type, cache account etc. hooks.beforeUseCachecalculate CacheInfo with HTTPRequesthooks.afterRenderUse CacheInfo to save RenderResult into cache of choicehooks.findCachefind cached RenderResult with CacheInfoCustom Render plugin
Taps
hooks.render, accept RenderContext, use the information to render the page with whatever you like, could be any UI library or some custom functions. Or if you want to bypass all existing hooks, you could:- Taps
hooks.receiveRequest, intercept certain request, generate your own RenderResult - Taps
hooks.beforeResponse, generate your own response based previous RenderResultData fetch plugin
Taps
hooks.beforeRender, fetch data and put inRenderContext.meta.initState. Support multiple RPC protocols other than HTTP, support fetch error handle, auto retry etc.Error Handle plugin
Taps
hooks.beforeResponse, handle RenderResult.type === ‘error’ scenario, could have error report, CSR downgrade, standardized 404 page etc.